 Educational Systems Theory
Educational Systems Theory Educational Systems Theory
Educational Systems Theory
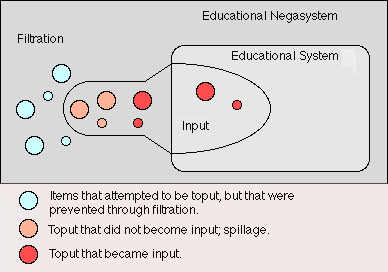
32.2 For example, prior to Public Law 94-142, some handicapped people were not allowed to attend public school. Hence, they were spillage.
32.3 Some students try to bring drugs and guns to school. If the guns an drugs are not allowed to enter school grounds and buildings, then they become spillage.
32.4 If parents attempt to send notes to their children's teachers, but those notes get lost on the way to school, then the parents' messages are spillage.
32.5 If an individual receives 100 electronic mail messages per day, but only has time to read a few, many messages are left unread. These neglected messages are spillage (toput that is not input)
32.6 The Smith Animal shelter can only house 95 pets, and has a rule that it will only accept pets from the local community. If a pet is brought in from 50 miles away, filtration will prevent it from becoming toput. If, however, a pet is brought in f rom down the block (it is toput), and the shelter must refuse it entry because it already has 95 pets, this pet is spillage.
32.7 A college or graduate student has a long list of reading material and homework assignment to complete, the work that is not completed is spillage.
#98. If educational system storeput increases and (filtration decreases or spillage decreases), then integration increases.
 Go to SIGGS Home Page.
Go to SIGGS Home Page.