 Educational Systems Theory
Educational Systems Theory Educational Systems Theory
Educational Systems Theory
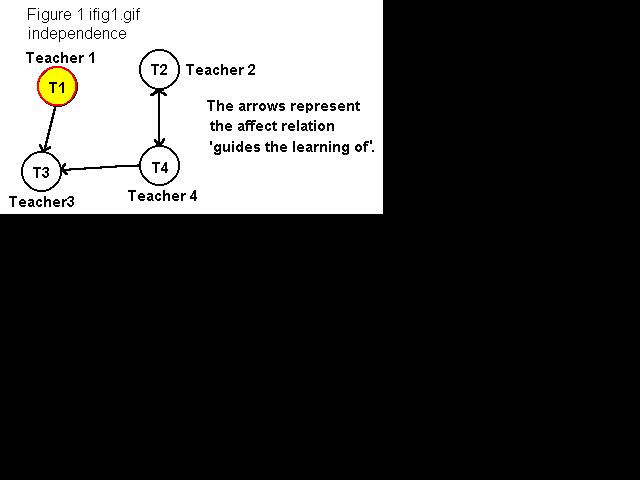
Another example of indepdence would be a social studies teacher who ignores instructions by the school board and superintendent to change his curriculum. With respect to the affect relation "decides curriculum", this teacher would have the property of independence.
#68. If educational system centrality is less than some value, then independence increases.
#164. If educational system independence increases, then stability is less than some value.
#168. If educational system independence increases and wholeness increases, then state steadiness is greater than some value.
#178. If educational system hierarchical order at a given time is greater than some value and size at a given time is greater than some value, then independence at a later time increases.
 Go to SIGGS Home Page.
Go to SIGGS Home Page.